Abstract
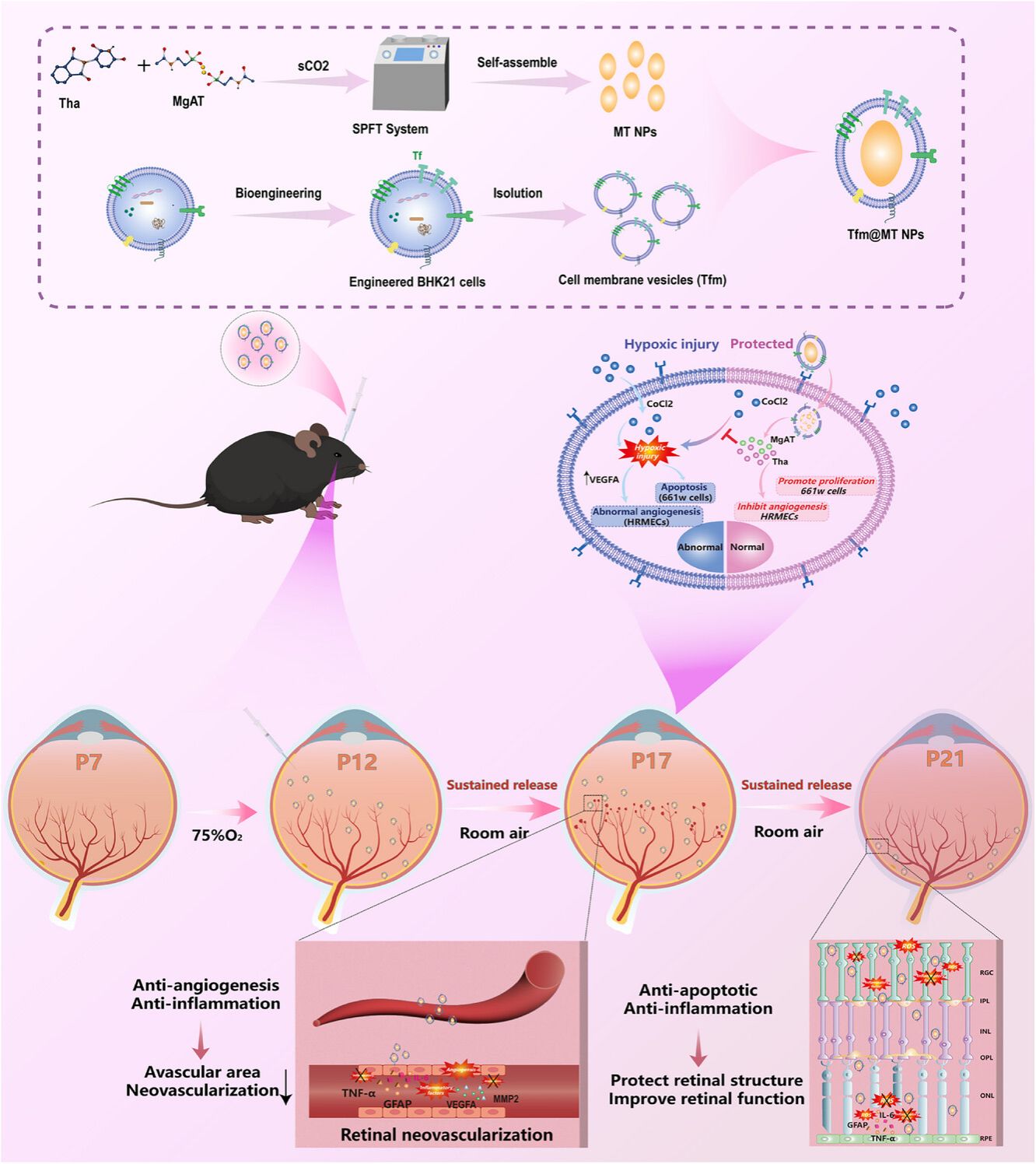
Retinal neovascularization (RNV) drives dual pathological cascades: structural destruction characterized by intraretinal/vitreous hemorrhages and tractional retinal detachment, alongside functional decline marked by progressive neurodegeneration and irreversible vision loss. Current clinical interventions for RNV face critical limitations in targeting specificity and therapeutic durability. To address this, we engineer magnesium acetyl taurate/thalidomide co-assembled nanoparticles (MT NPs) via Super-stable Pure Nanomedicine Formulation Technology (SPFT), constructing solvent-free, coordination-driven nanostructures with dual-drug loading. The MT NPs are further coated with transferrin-modified cell membrane vesicles (Tfm) to form targeted nanocomposites (Tfm@MT NPs). In oxygen-induced retinopathy (OIR) mouse models, Tfm@MT NPs demonstrated: (1) specific targeting to pathological vascular endothelia and retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) via transferrin receptor-mediated uptake, (2) sustained drug release exceeding 10 days, and (3) potent therapeutic effects in restoring visual functions. This study establishes a safe and effective targeted nanotherapeutic strategy for RNV, with significant translational potential for retinopathy treatment.
文章链接:https://doi.org/10.1002/agt2.70174