Abstarct
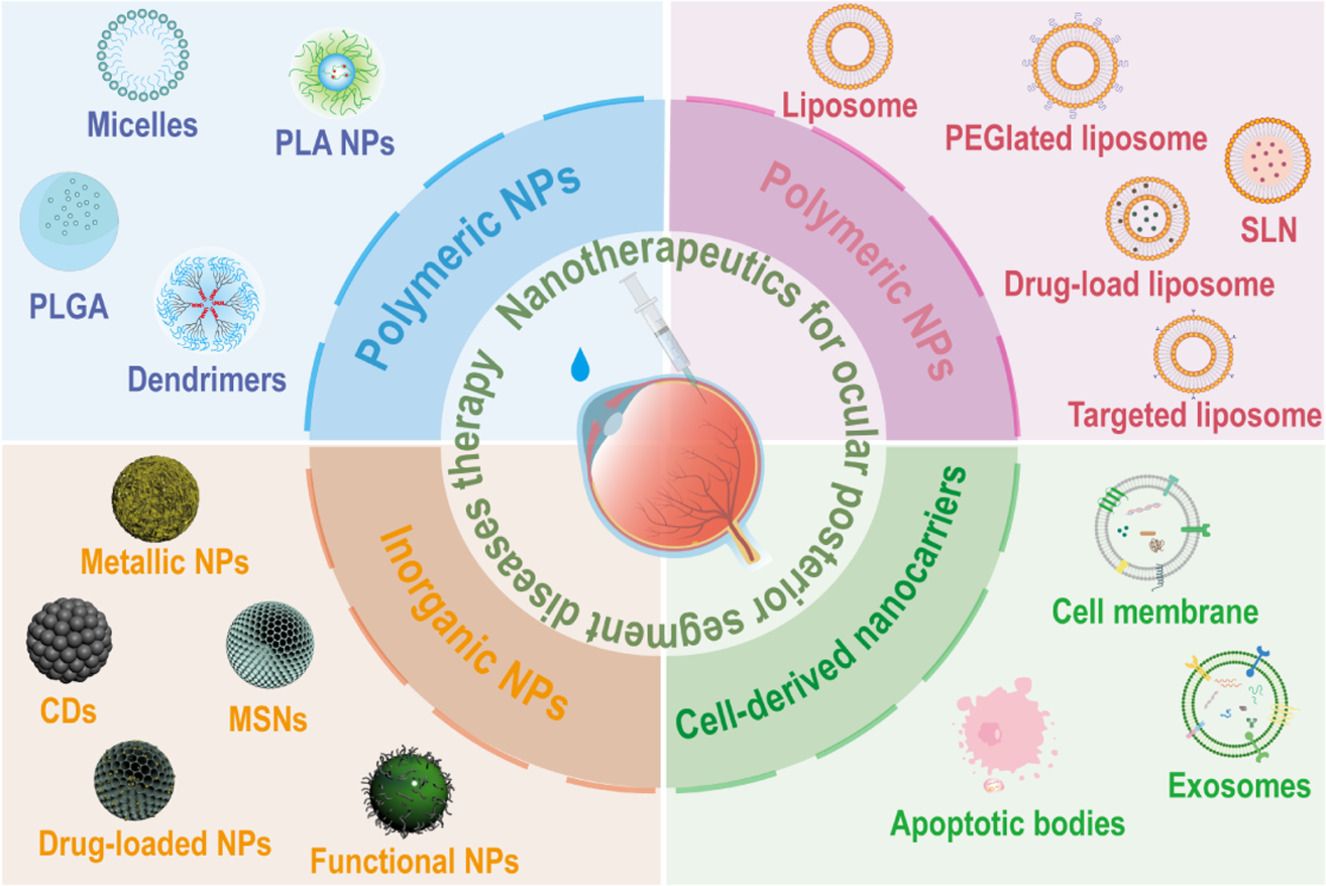
Ocular posterior segment diseases (OPSDs), including uveitis, glaucoma, retinitis pigmentosa (RP), fundus neovascular diseases (FNDs), and age-related macular degeneration (AMD), are major causes of global blindness. The eye's biological barriers often prevent conventional drugs from reaching the posterior segment effectively, while potentially causing adverse effects. Nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems (DDS) offer promising solutions, with their small size, tunable properties, and high biocompatibility enhancing drug permeability, stability, and targeted delivery. These systems may reduce administration frequency, prolong therapeutic effects, minimize side effects, and improve patient compliance. Unlike previous reviews, this article comprehensively examines novel nanocarriers for OPSD treatment. We first analyze small molecules, their nanocarriers, and administration methods based on recent two-decade research. Next, we compare nanocarrier stability, biocompatibility, ocular penetration, drug release kinetics, and formulation ease, emphasizing recent advances in design, preparation, and functional modification. Finally, by evaluating clinical applications and challenges, we discuss translational hurdles and future prospects for OPSD nanotherapeutics. Greater research efforts are needed to realize nanocarriers' full potential in OPSD treatment.
文章链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2025.111392