Abstract
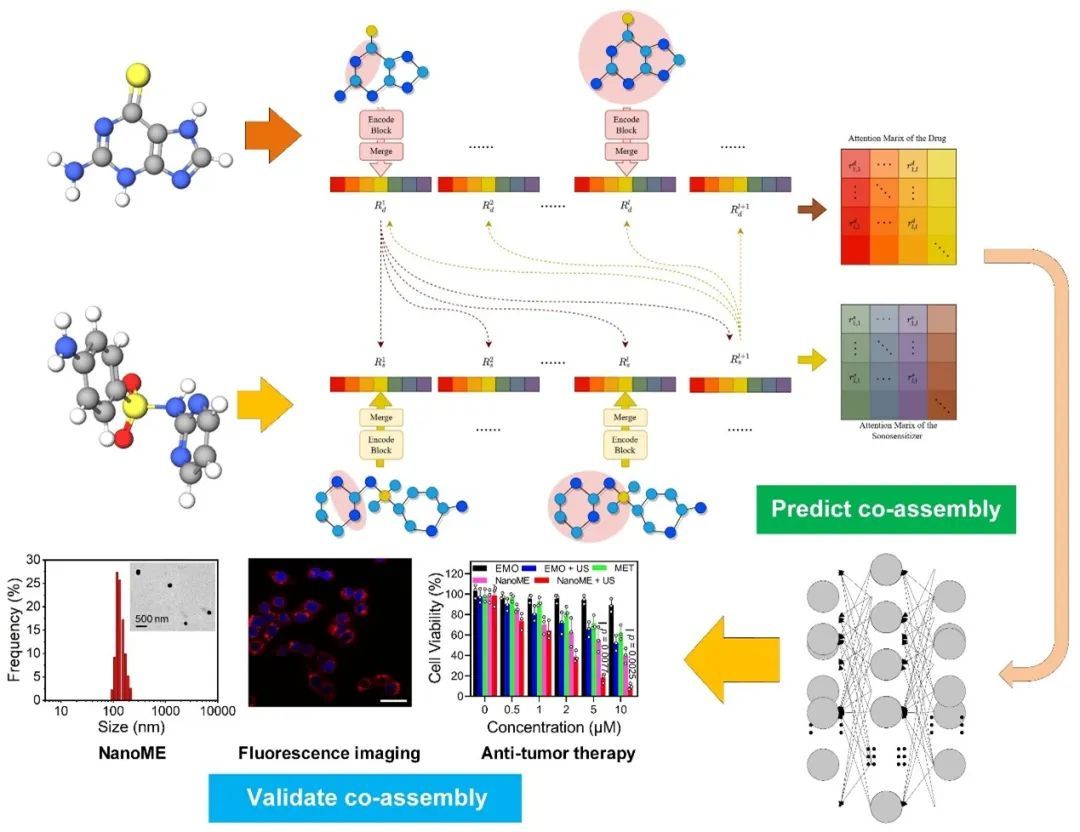
Drug co-assemblies have attracted extensive attention due to their advantages of easy preparation, adjustable performance and drug component co-delivery. However, the lack of a clear and reasonable co-assembly strategy has hindered the wide application and promotion of drug-co assembly. This paper introduces a deep learning-based sonosensitizer-drug interaction (SDI) model to predict the particle size of the drug mixture. To analyze the factors influencing the particle size after mixing, the graph neural network is employed to capture the atomic, bond, and structural features of the molecules. A multi-scale cross-attention mechanism is designed to integrate the feature representations of different scale substructures of the two drugs, which not only improves prediction accuracy but also allows for the analysis of the impact of molecular structures on the predictions. Ablation experiments evaluate the impact of molecular properties, and comparisons with other machine and deep learning methods show superiority, achieving 90.00% precision, 96.00% recall, and 91.67% F1-score. Furthermore, the SDI predicts the co-assembly of the chemotherapy drug methotrexate (MET) and the sonosensitizer emodin (EMO) to form the nanomedicine NanoME. This prediction is further validated through experiments, demonstrating that NanoME can be used for fluorescence imaging of liver cancer and sonodynamic/chemotherapy anticancer therapy.

文章链接:https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202502328
文章导读:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/uL001Q9wx38RgicJd-TV1Q