Abstract
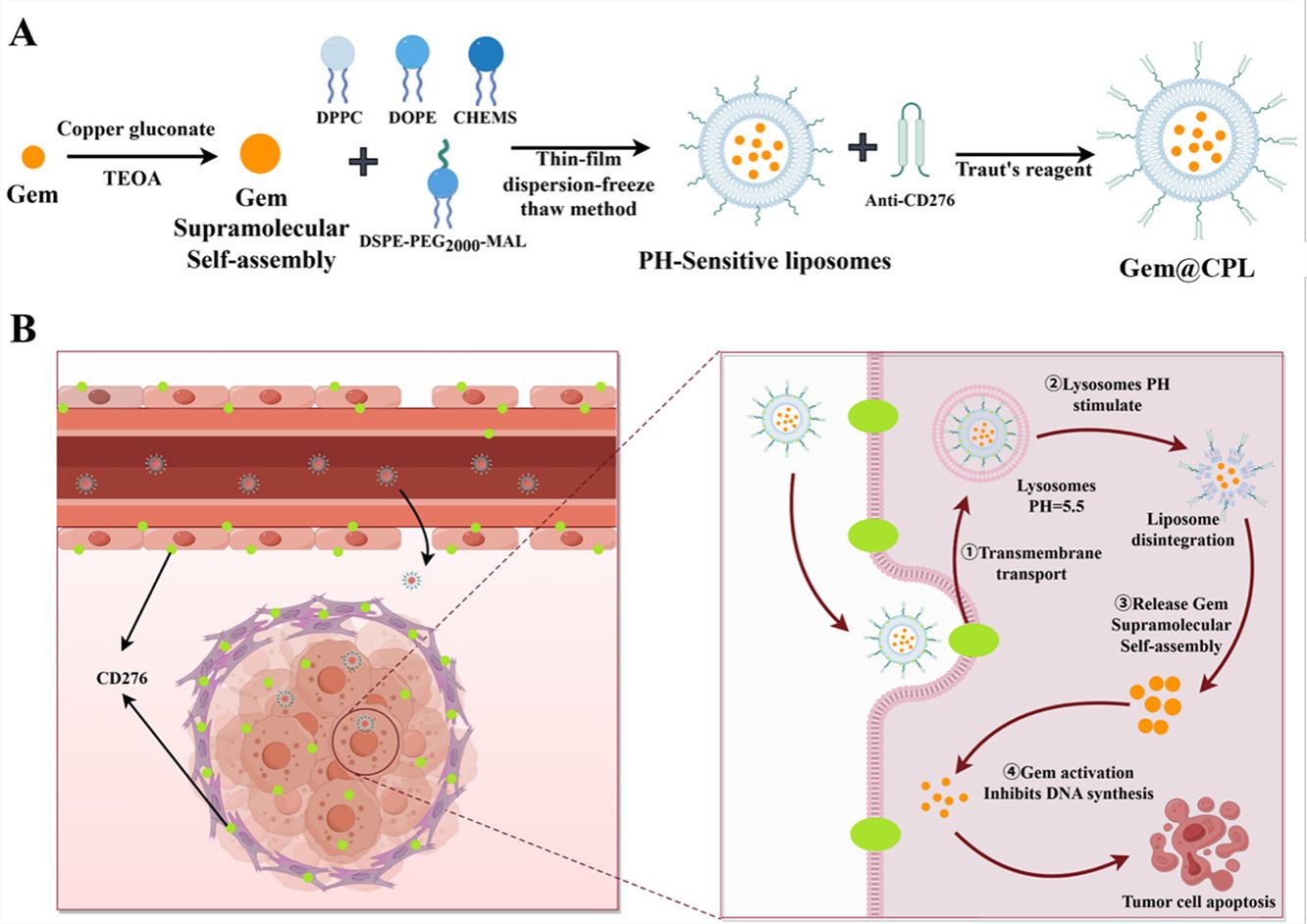
Gemcitabine (Gem) remains a cornerstone chemotherapy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, but its clinical efficacy is limited by poor pharmacokinetics, dense fibrotic stroma, and hypovascularization. While pH-responsive liposomes can enhance circulation and targeted drug release, their clinical application is hindered by low drug loading capacity and premature leakage of hydrophilic drugs. To address these challenges, we exploited the high and specific expression of CD276 on pancreatic cancer cells, tumor vasculature, and fibroblasts. We engineered a high-specificity and high-affinity anti-CD276 scFv, and developed a novel nanoplatform (Gem@CPL) that integrates pH-responsive and supramolecular assembly strategies with Gem, achieving 4-fold higher drug loading, improved stability, and tumor-specific release. Cellular and animal studies confirmed that Gem@CPL facilitates tumor-specific accumulation and CD276-mediated internalization, resulting in improved intracellular delivery and therapeutic efficacy. Pharmacokinetic analysis revealed a 2.26-fold prolongation of half-life (t₁/₂) and a significant reduction in volume of distribution (Vd) to 0.11-fold compared to free Gem, indicating superior systemic exposure and minimized off-target distribution. Gem@CPL increased anti-tumor activity by 1.77-fold, demonstrating its enhanced efficacy via sustained circulation and targeted delivery. By specifically targeting CD276, this platform minimizes systemic toxicity and potentially improving patient tolerability, offering promising prospects for clinical translation and better outcomes in pancreatic cancer treatment.
文章链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpx.2025.100452