Abstract
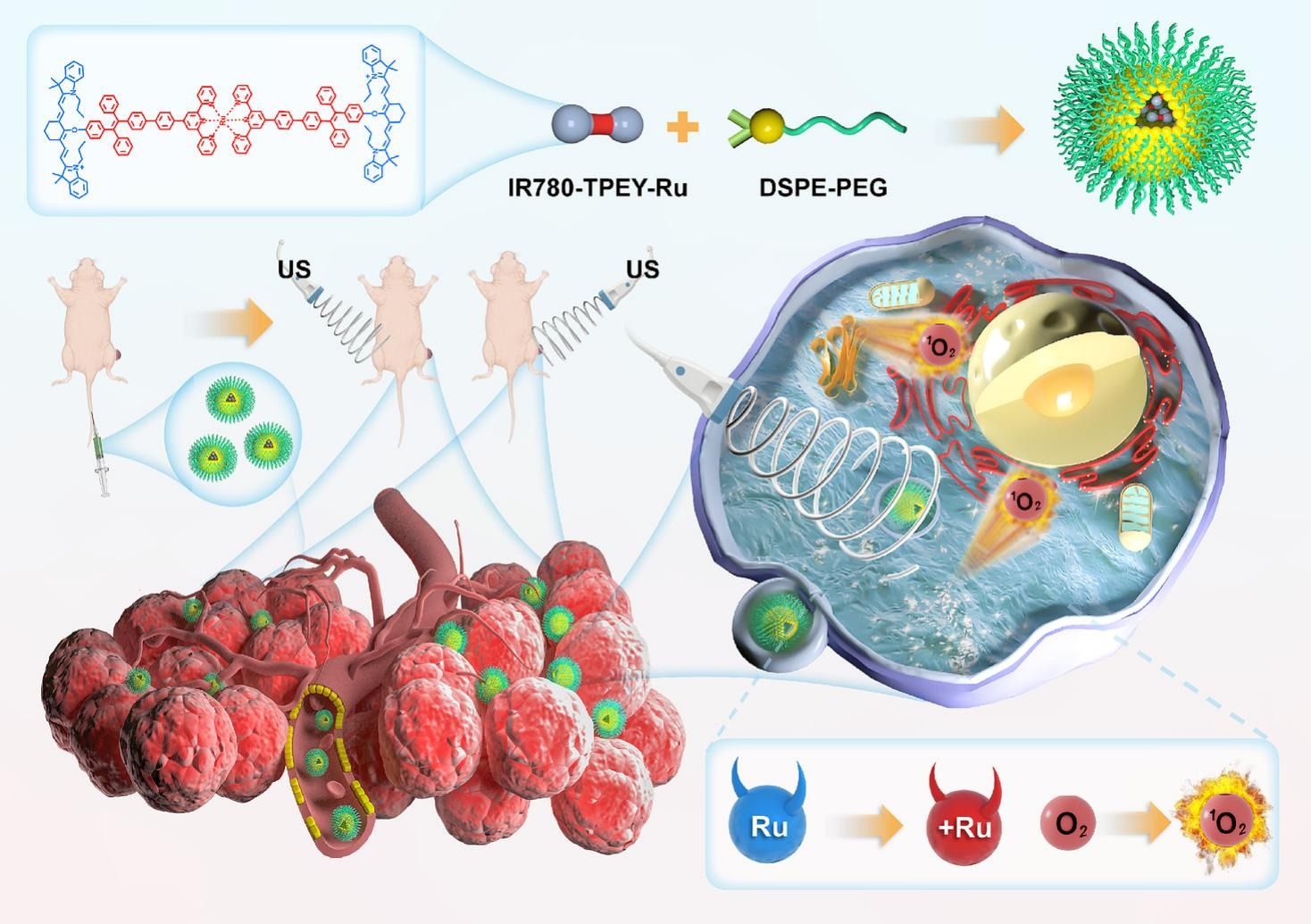
Recent advancements in nanomedicine have driven the development of multifunctional theranostic platforms for targeted cancer therapy. Sonodynamic therapy (SDT) holds a distinct advantage over traditional photodynamic therapy (PDT) by harnessing ultrasound-triggered sonosensitizer activation, enabling deeper tissue penetration for treating deep-seated tumors. In this study, we present IR780-TPEY-Ru, a nanoplatform specifically engineered for imaging-guided SDT to address challenges posed by deep-seated tumors. This platform is engineered through the synergistic integration of π-expansive ligands (IR780) with tetraphenylethylene (TPE), yielding a distinct Ru(II) complex that possesses exceptional electronic and structural properties, particularly in the near-infrared (NIR) region. Significant progress has been achieved through the integration of π-expanded tridentate ligands, which facilitate the generation of low-lying intraligand (3IL) and intraligand charge transfer (3ILCT) states, with ligands that enhance near-infrared absorption characteristics. The optimized IR780-TPEY-Ru exhibits both NIR-enabled bioimaging capabilities and exceptional therapeutic potential, particularly for deep-seated tumors, due to its sustained response to ultrasound stimulation. This study offers a promising strategy for developing tailored sonosensitizers for imaging-guided sonodynamic therapy.
文章链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2025.107415