Abstract
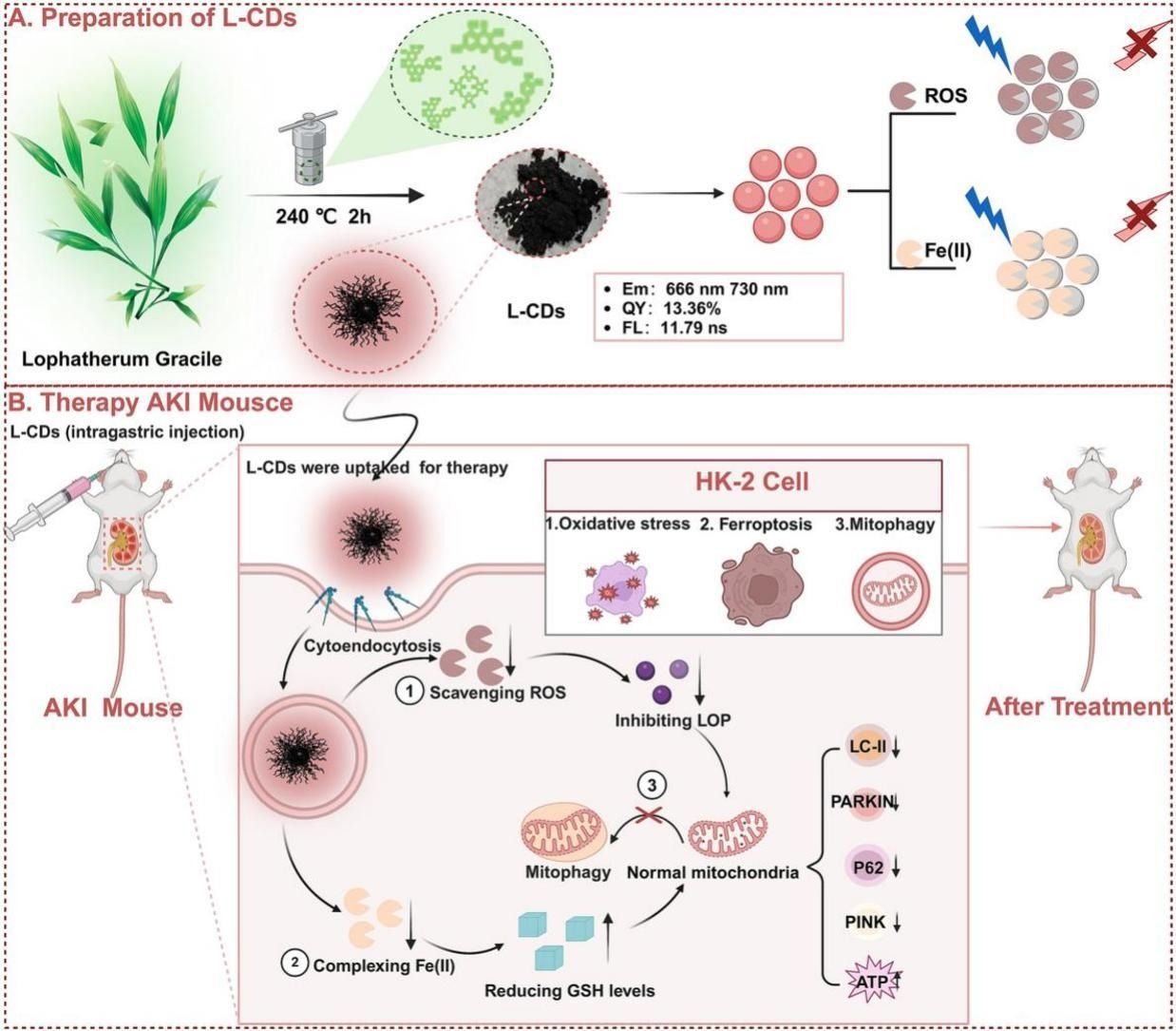
Carbon dots (CDs) based-biomass are known for their excellent safety but often face challenges such as short emission (Em) wavelength and low quantum yield (QY). Here, using the traditional Chinese medicinal lophatherum gracile as a carbon source, we combined conventional decoction techniques with CDs preparation methods to obtain safe and green CDs (Lophatherum-Gracile driven near-infrared carbon dots, L-CDs) for the first time with an Em peak at 666 nm, a shoulder peak at 730 nm, and a QY of 13.36 %. L-CDs showed remarkable stability, safety, and resistance to photobleaching. Notably, it effectively quenched reactive oxygen species (ROS) and exhibited specific sensitivity to Fe(II). Additionally, L-CDs exhibited potential in treating ferroptosis-related inflammation and inhibiting mitophagy, and they were found to be effective in preventing and treating cisplatin (CDDP)-induced acute kidney injury (AKI). These effects were comparable to those of commercially available ferroptosis therapies-Ferrostatin-1 (Fer-1) and deferoxamine (DFO). Overall, our work presents novel, safe, and eco-friendly near-infrared L-CDs that can be effectively utilized for identifying cellular organelle and in vivo imaging, as well as for treating ferroptosis, mitochondrial-related inflammation, and chemotherapy-induced AKI. These findings broaden the potential applications of CDs in biomedical diagnosis and therapy, intending to advance clinical development.
文章链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1385894725034631#ab010