Abstract
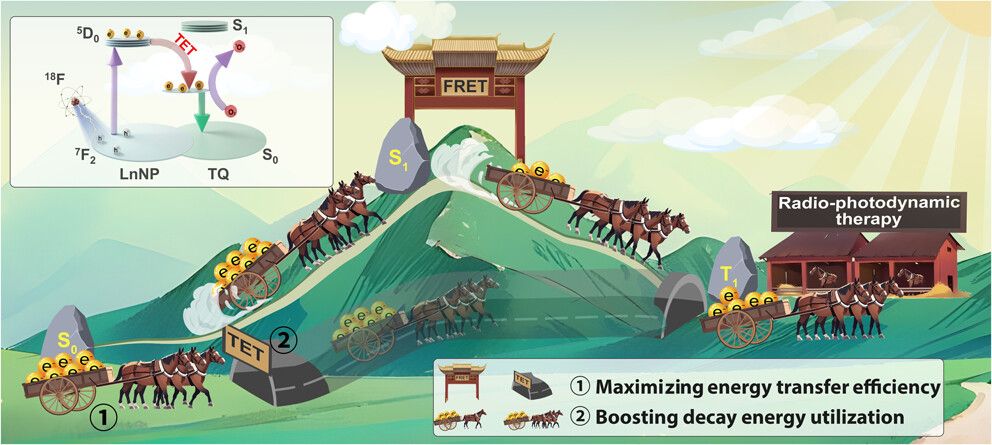
Cerenkov light (CL), utilized as an internal excitation source for photodynamic therapy (PDT), addresses the limitations of laser penetration and has substantial potential for seamlessly integrating clinical radiotheranostics with phototheranostics. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of CL-mediated PDT is significantly hindered by challenges, such as the low intensity of CL and inadequate energy transfer between the CL donor and photosensitizers (PSs). In this study, a novel approach is introduced for enhanced radionuclide-activated radio-photodynamic therapy utilizing a hybrid nanoparticle system composed of lanthanide nanoparticles and an aggregation-induced emission photosensitizer (AIE PS), designated LnNP–TQ NPs. This system enables lanthanide nanoparticles to optimize the decay energy of radionuclides, effectively sensitizing the AIE PS through triplet energy transfer (TET)-mediated processes with an efficiency approaching 100%. When activated by the clinical radionuclide 18F for positron emission tomography imaging, the LnNP–TQ NPs substantially inhibited tumor growth via effective singlet oxygen (1O2) generation. This strategy, which optimally harnesses radionuclide energy and achieves efficient energy transfer, offers a promising pathway for enhancing radiotherapy–phototherapy efficacy in tumor treatment.
文章链接:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.4c18033