Abstract
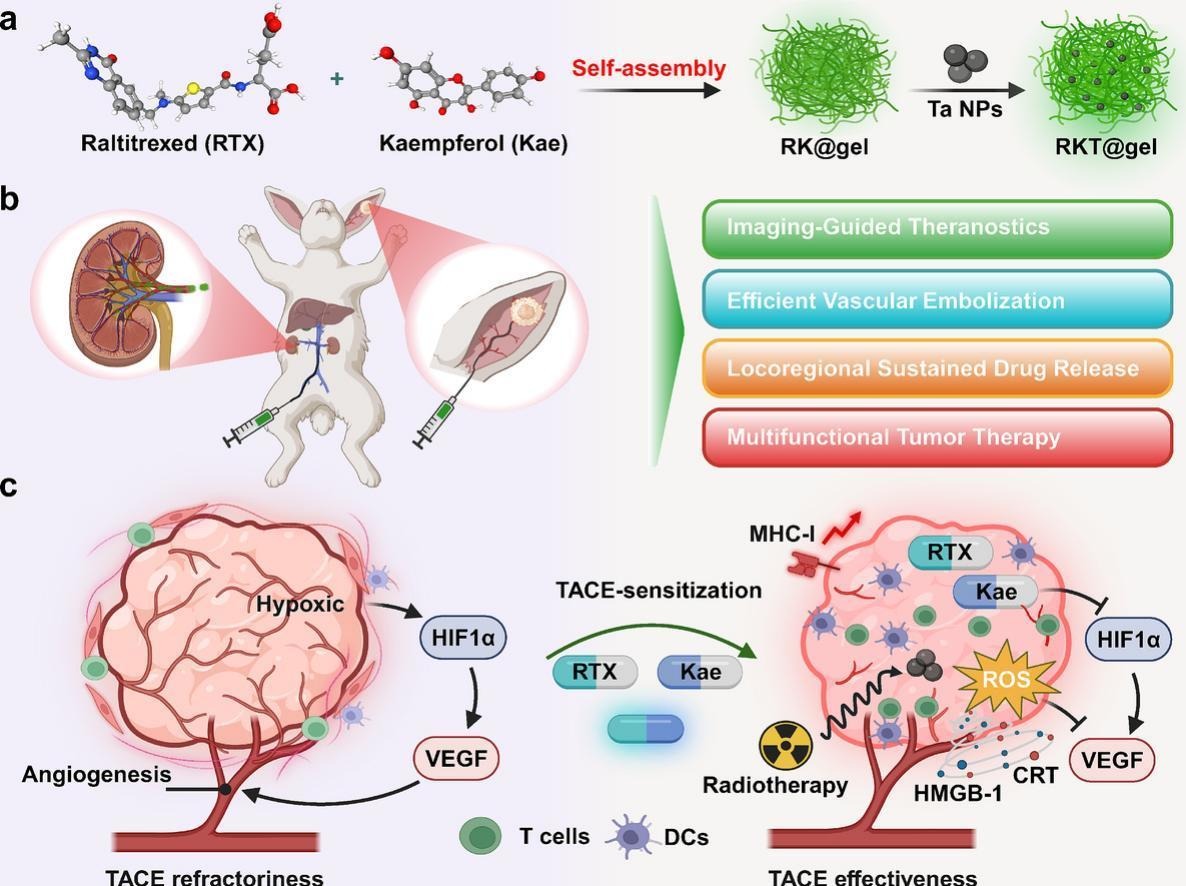
Hydrogel, as a promising embolic material for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), may fully embolize both major vessels and peripheral microvessels. A self-assembling hydrogel composed of chemotherapeutic drugs offers significant clinical benefits without carrier introduction. Herein, we developed a sustained drug-releasing complex hydrogel (RKT@gel), which was fabricated by the self-assembly of raltitrexed chemotherapeutic drugs (R@gel), along with the incorporation of kaempferol and tantalum nanoparticles (Ta NPs). Kaempferol enhances the mechanical strength of R@gel and inhibits hypoxia-induced angiogenesis post-embolization, improving embolization effectiveness. In addition to enabling X-ray-guided transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), Ta NPs enhance radiation sensitivity. These synergistic effects of RKT@gel not only significantly induce immunogenic cell death, thereby enhancing the activation of dendritic cells, but also activate major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I)-mediated antitumor immune recognition and cytotoxicity. In vivo, RKT@gel achieves enhanced tumor deposition and sustained drug release, effectively suppressing tumor progression. Additionally, when combined with radiotherapy, RKT@gel achieves efficient antitumor immunoactivation. Overall, this versatile composite hydrogel not only achieves effective embolization therapy but also substantially triggers antitumor immune responses with good biocompatibility. This multifunctional design provides a TACE-based multidisciplinary strategy for HCC.
文章链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168365925000987#ab0015
文章导读:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/lRBw1TGw4CjoqwepAu5Irw