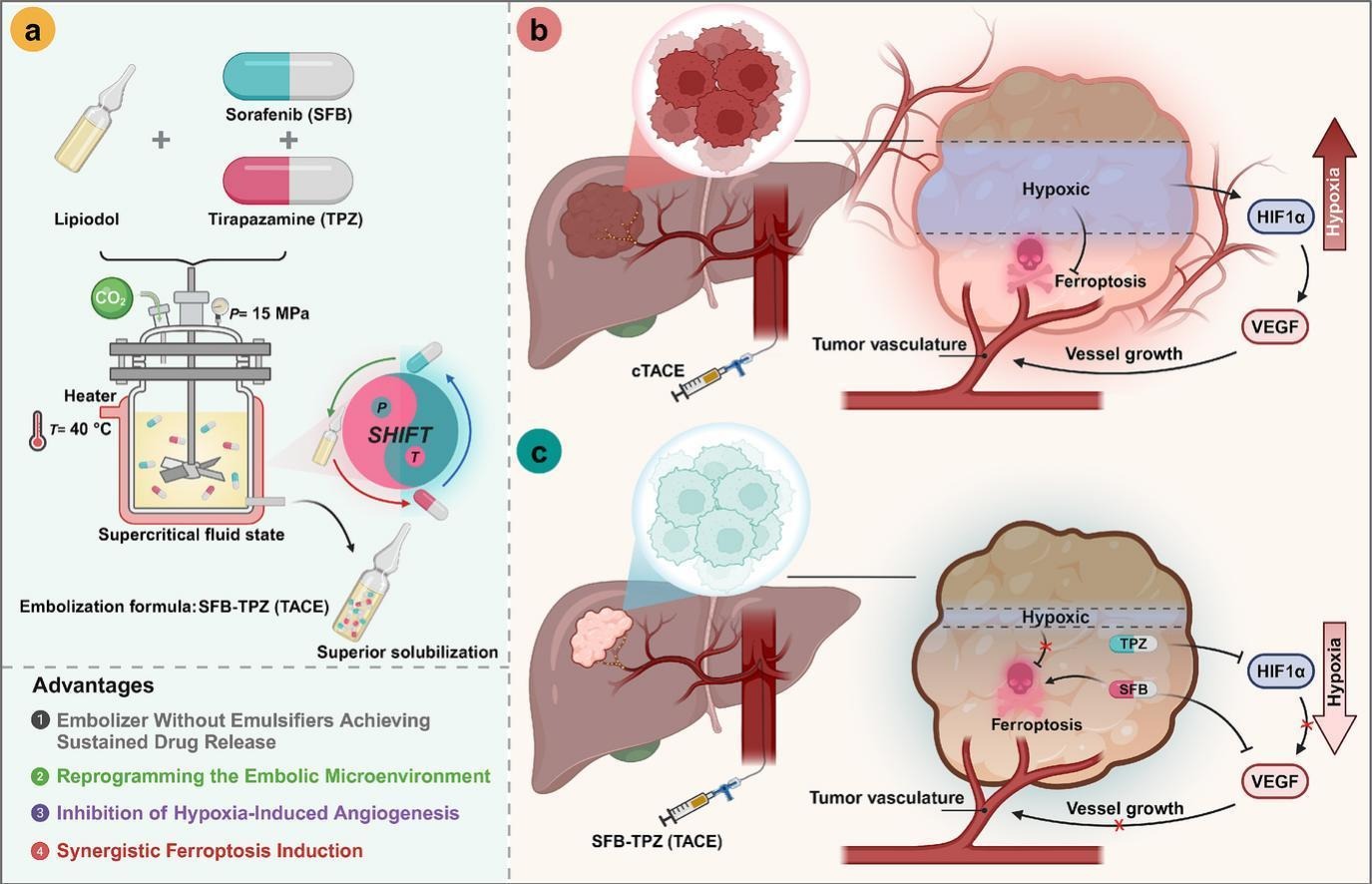
Abstract
Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is the principal treatment option for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the hypoxic microenvironment following TACE can promote angiogenesis and suppress tumor ferroptosis, resulting in an unfavorable prognosis. Tirapazamine (TPZ), a hypoxia-activated prodrug with specific cytotoxicity for hypoxic cells, making it a potential candidate for TACE. To develop an effective hypoxia-responsive drug delivery platform for TACE, we propose a novel lipiodol embolic formulation that integrates TPZ and sorafenib (SFB) by super-stable homogeneous intermixed formulation technology (SHIFT). This approach achieves the manufacture of embolic agents with stable drug dispersion characteristics, fulfilling the need for sustained drug release in TACE. The prolonged tumor penetration of TPZ exhibited embolization-responsive tumor killing, and its combination with SFB can suppress hypoxia-induced angiogenesis and trigger tumor ferroptosis, maintaining low oxygen levels, thereby boosting the therapeutic efficacy of TPZ. Conversely, TPZ can combat the resistance to SFB in hypoxic tumor cells. In summary, this study developed a novel embolization drug formulation based on embolic hypoxic microenvironment. The synergistic mechanism of TPZ and SFB enhances the therapeutic effects of hypoxia-activated prodrugs and mitigates the adverse effects of hypoxia.
文章链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168365925000847?via%3Dihub#ab0005