Abstract
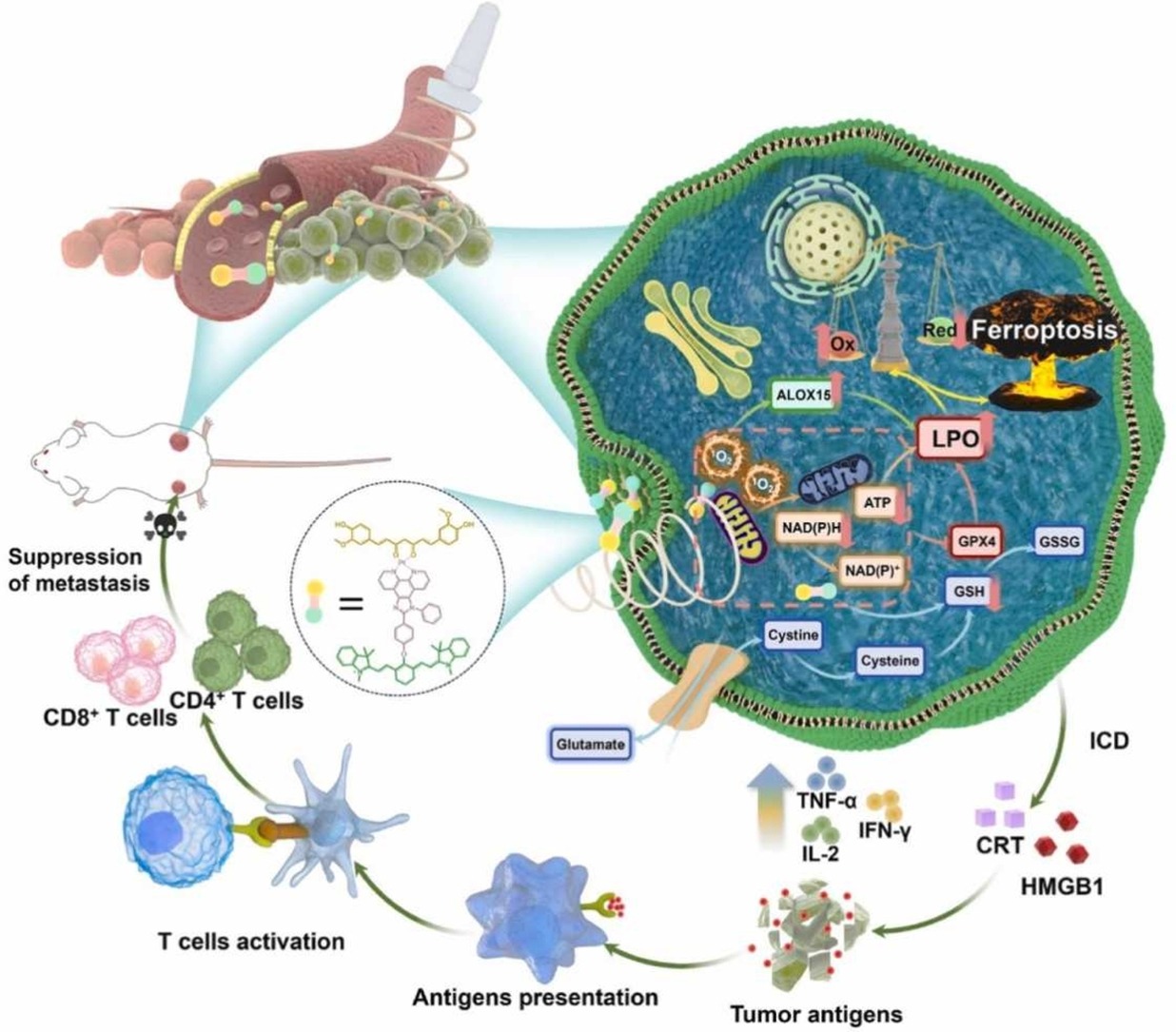
Drug design and mechanisms are essential for advancing our understanding of sonosensitizer development, the biological processes underlying anti-tumor responses, and guiding optimal treatment strategies. This article highlighted a remarkably efficient organometallic compound (IRCur-Pt), which has shown remarkable efficiency in reducing toxicity and increasing sono-sensitivity. Our research offers a theoretical framework to explain the superior performance of IRCur-Pt, highlighting its precise targeting of mitochondria and its ability to generate a substantial amount of 1O2 upon ultrasound stimulation, directly killing cancer cells. Notably, IRCur-Pt disrupted mitochondrial structure, resulting reduced ATP capacity, interference with NADPH, depletion of GSH, inhibition of GPX4 activity, accumulation of lipid peroxidation, and subsequent occurrence of ferroptosis. Furthermore, proteomic analysis strongly supported IRCur-Pt’s anti-tumor mechanisms in vivo, confirming the activation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) ferroptosis signaling pathways, along with T cell receptor signaling pathways. Consistent anti-tumor effects were observed in animal models. In systemic immune assessments, IRCur-Pt+US effectively activated adaptive T cells while suppressing the proliferation of Treg cells, highlighting its substantial therapeutic potential. Through a multifaceted approach, IRCur-Pt demonstrated outstanding anti-tumor performance under US irradiation. This study comprehensively introduced novel perspectives for drug design, inducing cancer cell apoptosis, amplifying ferroptosis, triggering systemic immunity, and providing an innovative avenue for cancer treatment.
文章链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1748013224002251